Wildflowers come in an incredible array of colors, but pink gold hues hold a particular allure. So, What Wildflowers Are a Pink Gold Color exactly? These delicate shades evoke warmth and beauty, drawing attention in wild landscapes and curated gardens alike. From the pink evening primrose to the Indian paintbrush, pink-gold wildflowers captivate both environmental enthusiasts and garden lovers. In this exploration, we’ll discuss their ecological importance, conservation status, and the impact of climate change on these unique blooms.
The Significance of Pink and Gold in Wildflowers
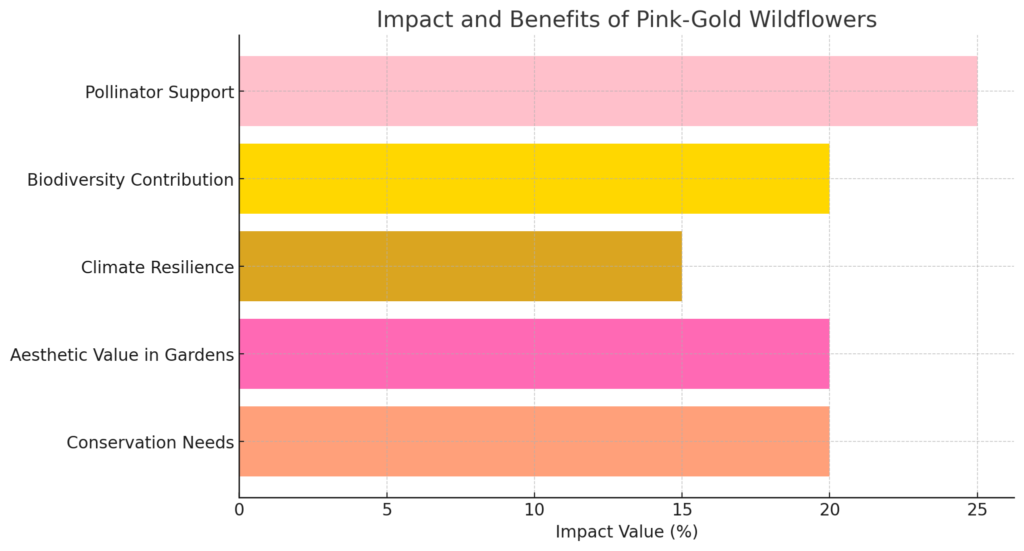
Wildflowers with pink and gold hues are celebrated for their beauty, but their significance runs deeper. These colors play an essential role in ecological signaling. Pink and gold shades attract various pollinators, including bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds, which rely on visual cues to locate nectar-rich flowers. This color combination is relatively rare in the wild, making it a prized sight for conservationists and nature lovers.
The Appeal of Pink Gold Wildflowers
The appeal of pink-gold wildflowers extends beyond aesthetics. These colors represent a blend of warmth and vibrancy, evoking sunset hues that stand out against green landscapes. Gardeners often choose pink-gold wildflowers to add unique visual elements to their landscapes, while naturalists appreciate them for their role in supporting biodiversity. In certain cultures, pink-gold wildflowers also symbolize harmony and tranquility, adding an emotional layer to their allure.
Native Wildflowers with Pink Gold Hues
Several native wildflowers boast this unique color palette, thriving in North American landscapes and supporting local ecosystems.
1. Pink Evening Primrose (Oenothera speciosa)
Pink evening primrose is a lovely wildflower that grows throughout central and southern United States. Its pale pink petals with golden centers open in the evening, attracting nighttime pollinators like moths. Not only is this flower visually striking, but it also plays a vital role in local habitats, providing nectar for various insects.
2. Blanket Flower (Gaillardia pulchella)
Native to the plains and prairies, the blanket flower features fiery colors that range from deep red to a pinkish gold. This wildflower is resilient, thriving in sandy soils and drought-prone areas. The blanket flower attracts bees, butterflies, and other pollinators, making it a favorite among conservationists focused on promoting biodiversity in restored habitats.
3. Indian Paintbrush (Castilleja coccinea)
The Indian paintbrush is known for its bright pink and orange bracts, which can resemble delicate brush strokes. Found in grasslands and open woodlands, this wildflower is partially parasitic, obtaining nutrients from neighboring plants. Despite this unusual trait, it supports local pollinators and adds vibrant color to open landscapes.
Rare and Endemic Pink Gold Wildflowers
Certain pink-gold wildflowers are rare or endemic, making them particularly valuable in conservation efforts.
1. Desert Mariposa Lily (Calochortus kennedyi)
The desert mariposa lily is a rare find in arid regions of the southwestern United States. Its cup-shaped pink flowers with golden centers are adapted to thrive in rocky soils. This lily is vulnerable to habitat loss due to urban development and climate change, making it a conservation priority.
2. Bitterroot (Lewisia rediviva)
Bitterroot grows in mountainous regions and is recognized for its soft pink petals tinged with gold. The flower is celebrated in Native American culture and has spiritual significance. Bitterroot’s resilience in harsh conditions speaks to its adaptability, though it remains endangered due to habitat fragmentation.
3. Pink Fairy Orchid (Caladenia latifolia)
The pink fairy orchid is a delicate wildflower native to Australia, known for its pale pink petals and subtle golden markings. This orchid’s rarity and specific growth requirements make it vulnerable to climate fluctuations. Conservation efforts focus on protecting its natural habitats and supporting pollinator species that contribute to its reproduction.
Pink Gold Wildflowers in Gardens and Landscaping
Incorporating pink-gold wildflowers into gardens and landscapes brings aesthetic and ecological benefits. These flowers can transform spaces by adding pops of warm, unique colors that attract visitors and pollinators alike.
Benefits of Pink Gold Wildflowers in Gardens
Pink-gold wildflowers are not only visually appealing but also offer ecological advantages. They create habitats for pollinators, promoting biodiversity even in urban settings. Gardeners who choose native pink-gold wildflowers contribute to local ecosystems by providing food sources for bees and butterflies. These wildflowers also require minimal maintenance, often thriving in low-water conditions and supporting sustainable landscaping practices.
Conservation of Pink Gold Wildflowers
Conserving pink-gold wildflowers involves understanding the threats they face and implementing strategies to protect their populations.
Threats to Wildflowers
Wildflowers face numerous threats, including habitat loss, invasive species, and climate change. Urban expansion often leads to habitat fragmentation, which disrupts the natural landscapes these flowers depend on. Additionally, pollution and pesticide use can harm wildflower populations and the pollinators they attract, resulting in declining biodiversity.
Conservation Strategies for Pink Gold Wildflowers
Conservationists are implementing various strategies to protect these unique wildflowers, from habitat restoration to public education.
1. Habitat Restoration
Restoring habitats involves replanting native species and removing invasive plants that compete for resources. By restoring natural habitats, conservationists create environments where pink-gold wildflowers and other native plants can flourish, supporting a diverse range of species.
2. Seed Collection and Propagation
Seed banks and propagation programs play a vital role in conserving endangered wildflowers. Collecting seeds from rare pink-gold wildflowers and propagating them in controlled environments allows conservationists to reintroduce these plants into their native habitats when conditions are favorable.
3. Public Education and Involvement
Public education is essential for effective conservation. VoicesofConservation.org emphasizes the importance of educating communities about the value of wildflowers and encouraging people to participate in conservation efforts. Community involvement, such as local planting projects and citizen science initiatives, can significantly impact conservation success.
4. Legal Protections and Conservation Reserves
In many regions, legal protections are established to prevent the over-harvesting or destruction of rare wildflowers. Conservation reserves provide protected areas where pink-gold wildflowers and other native species can thrive without the threat of human interference.
The Role of Pink Gold Wildflowers in Supporting Pollinators
Pink-gold wildflowers are crucial for the health of pollinator populations. They provide nectar and pollen for bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds, supporting the reproduction of these vital species.
Wildflowers and Pollinator Health
Pollinators are essential for the survival of numerous plants, including crops. Wildflowers with pink-gold hues attract pollinators through their vibrant colors, helping maintain healthy ecosystems. By supporting pollinators, pink-gold wildflowers contribute to the stability of local and agricultural ecosystems.
Supporting Native Pollinators
Supporting native pollinators is a conservation priority, as many face threats from habitat loss and pesticide exposure. Pink-gold wildflowers play a role in this effort by offering food sources specific to native pollinators, such as solitary bees and certain butterfly species. Cultivating these flowers in gardens can help bolster pollinator populations and enhance biodiversity.
Climate Change and Its Impact on Pink Gold Wildflowers
Climate change poses significant risks to wildflower populations, affecting blooming patterns, habitats, and the health of associated species.
Changes in Blooming Periods
As temperatures rise, wildflowers are blooming earlier in the year. This shift can disrupt the synchronization between wildflowers and pollinators, leading to fewer successful pollination events. Pink-gold wildflowers may bloom out of sync with native pollinators, impacting their survival and reproduction rates.
Habitat Shifts
Climate change is causing habitat ranges to shift, forcing pink-gold wildflowers to adapt to new environments or risk extinction. Some wildflowers may move to higher elevations or cooler regions to survive, but not all species can adapt quickly. Conservation efforts must focus on preserving diverse habitats to provide refuges for climate-affected wildflowers.
Conclusion: What Wildflowers Are a Pink Gold Color?
Pink-gold wildflowers bring beauty and ecological value to landscapes, serving as food sources for pollinators and supporting biodiversity. By understanding the significance of these colors and the unique species that exhibit them, we can better appreciate their role in the environment. Conservation of these wildflowers is essential, particularly in the face of threats like habitat loss and climate change. By protecting these plants and their habitats, we contribute to the resilience and diversity of natural ecosystems.